Mixing is all about shaping audio frequencies. The goal is to blend all the frequencies together and make them sound their best.
Resonant frequencies are the aural poisons that lurk inside your mix. They cloud your mix with unwanted, unmanageable frequencies, steal your precious headroom, and more — and they render your project unpleasant to listen to.
So, what are resonant frequencies, and what can you do about them?
In this article, we’re going to cover everything you need to know to vanquish unwanted resonant frequencies once and for all, and as a result, create cleaner-sounding mixes.

What is Resonance?
Before we discuss how to solve problems related to acoustic resonance, we should first explain what resonance is.
The book Fundamentals of Physics describes resonance as "the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of a periodically applied force is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts."
In other words, resonance occurs when a created frequency interacts with the natural frequency of your room, playback system, or something within your mix itself. You'll generally perceive this as an out-of-control vibration, such as feedback, or a buildup of a specific frequency or set of frequencies.
If your room or playback system are the cause of the unwanted resonances, you'll need to solve those problems physically with proper sonic isolation and acoustic treatment. However, if the issue is contained within your mix, you'll need to perform some surgical correction.

Common Types of Resonances
Low-frequency Resonance (Hum)
If you can hear an unpleasant hum-like sound in the lower end of your track's frequency spectrum, this is caused by low-frequency resonance. This type of hum is a true headroom killer, and it will lend a weak, quiet quality to your mix, regardless of what volume you play it back at.
Worse yet, when you increase the gain, the hum gets even louder! If you want a loud, punchy mix, it's essential that you take care of low-frequency resonances.
High-frequency Resonance (Notch Frequencies)
Notch frequencies cause high-frequency resonance in the 10kHz to 15kHz range. If your tracks produce harsh, ringing artifacts, this is likely why.
High-frequency resonance will cause near-immediate listening fatigue, and it will make your mix very unpleasant to listen to.

Why Do Resonances Affect Your Mix?
If your audio contains undesirable resonances — and it most likely does — you'll have a difficult time achieving an accurate mix. You might as well be monitoring with a couple of tin cans.
Remember, if you can't hear it; you can't mix it.
What's more, unwanted resonances can result in an ear-splitting or muffled sound, with harsh or buried upper mids and lows that push a subwoofer painfully past its limits.
On top of that, these runaway frequencies can wreck the dynamics of the affected track, and they can mask other elements in your mix, which throws your entire project off kilter.
Removing annoying resonances from your tracks is a guaranteed way to yield a clearer, more accurate mix that's much more pleasant to listen to and much easier for a mastering engineer to work with.

How to Get Rid of Resonances (The Hard Way)
The first step in removing unwanted resonances is to identify them.
Begin by instantiating a dynamic EQ plug-in in a track and creating a large (+15dB or more) EQ boost with a narrow Q bandwidth.
Solo the affected track. Then, while your mix is playing, sweep around the frequency spectrum and listen for any annoying droning or ringing frequencies that seem to be dominating the sonic spectrum.
When you locate a resonant frequency, place a frequency band on that spot. After that, lower the gain on the frequency band — -3dB is a good starting point, but use your ears.
Don't overdo it! If you get too heavy handed with this, you'll end up with a hollow, unnatural, low-quality sound.
Now repeat the process until you locate and attenuate all the resonances on every track in your mix. You may also have to repeat the process on your master bus.
Be patient, this could take a while! That said, it's an essential part of the mixing process.

How to Get Rid of Resonances (The Easy Way)
Locating and dialing out resonances the old-fashioned way is an involved, time-consuming endeavor. That's why we created RESO.
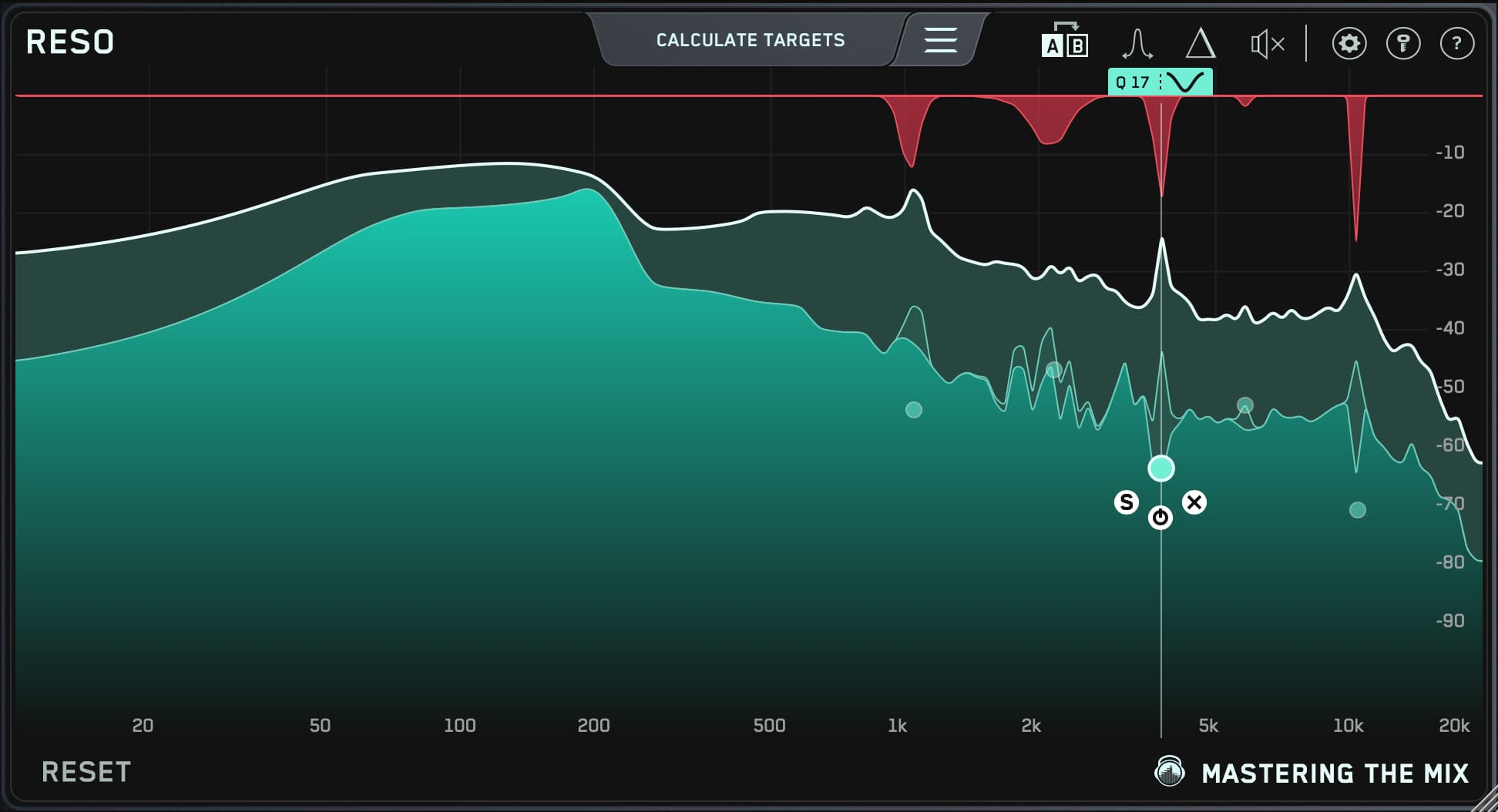
RESO is an easy-to-use plug-in that automatically finds and eliminates the problematic resonances in your mix. Best of all, its super-transparent processing won't damage the sound of your hard-earned mix.
What's more, RESO is an absolute breeze to use. Simply instantiate it on a vocal, synth, or percussion track, on a bus, or even as part of your mastering chain, then click the "Calculate Targets" button.
This time-saving plug-in automatically analyzes your audio, locates problematic resonant frequencies, and supplies you with "Target Nodes," as well as helpful setting suggestions for the plug-in's parameters — no inefficient EQ sweeps required.

How Does RESO Work?
RESO works by sampling the input spectrum multiples times per second. It then automatically creates a record of maximum frequency magnitudes that are statistically higher than neighboring frequencies.
And it's easy to use — to begin processing, click "Engage Targets" to engage the nodes. You can also click the targets one by one.
From there, you can tweak the nodes to suit your project and your preferences. You can also create nodes manually by double-clicking on RESO's interface.
You can move nodes freely around the spectrum, and they're a breeze to adjust.
You can easily lock the frequency by holding your computer's "Control" button before moving the node. You'll appreciate how this maintains your set frequency while you vertically adjust the amount of dynamic processing.
Likewise, you can lock the peak reduction and adjust the frequency by holding your computer's "Shift" button before moving the node horizontally.
What's more, every time you create a node, RESO automatically optimizes its Q for the best sound. And when you move the node around, it continuously updates the Q.
And if you're the tweaky type, you can adjust the Q manually by scrolling while hovering over the node.

Doing It the Old-fashioned Way
If you're an advanced engineer who prefers a more hands-on approach, RESO makes old-school frequency sweeping a piece of cake.
Simply engage the "Frequency Sweep" function, and your mouse position will determine which frequency is being boosted. You can then engage nodes on the fly whenever you encounter an offending resonance.

How Does RESO Sound?
RESO offers true world-class sound, offering the perfect balance between CPU use and low phase distortion, transient smearing, and pre- and post-ringing.
RESO's filters deliver a near-linear response, along with a negligible level of phase distortion — especially when you compare them with competing minimum phase filters. What's more, you'll experience very little pre- and post-ringing with higher Q values.
Beyond that, RESO contributes very little harmonic distortion, ensuring that your tracks — and your full mixes — achieve the best sound possible. If you crave maximum clarity and transparency, you'll be blown away by RESO.

Conclusion
Whether you're a seasoned pro or a bedroom producer, cleaning up the resonances in your mix is essential.
Skip this important step in the mix process, and you'll never achieve the loud, punchy, cohesive sound you're aiming for. Perform this step incorrectly, and you'll end up with wimpy, hollow-sounding mixes.
Our RESO plug-in provides you with a fast, easy way to tackle resonances, while also supplying you with convenient features and industry-leading sound.